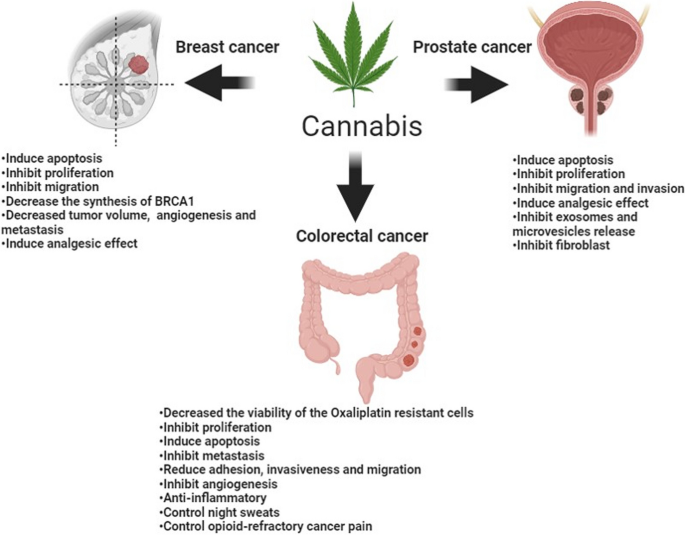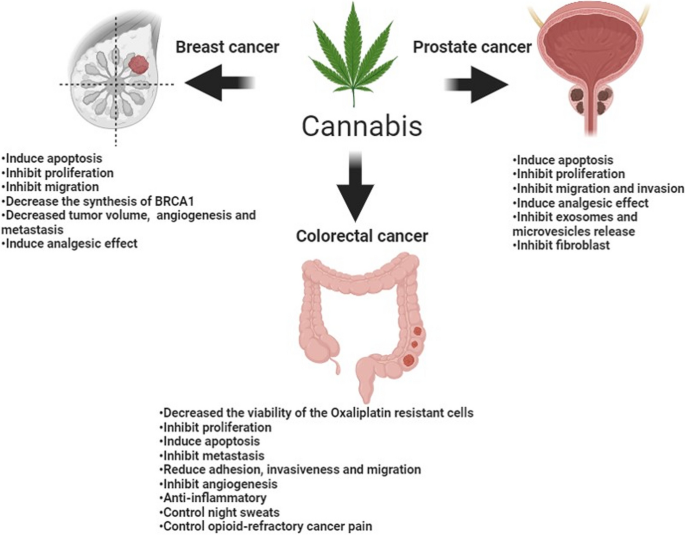
Online Security Verification: A Gateway to Trust in the Digital Age
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, a seemingly simple message requiring users to complete a security verification has grown from a minor annoyance into a key player in ensuring the safety and integrity of online interactions. While at first glance the prompt—”Please complete security verification”—may seem like nothing more than a technical necessity, a closer look reveals an interplay of legal, technical, and ethical concerns that are both fascinating and full of challenges. This opinion editorial explores the evolution of online verification protocols, the fine points behind their implementation, and the legal implications of this process, all while reflecting on the balancing act between security and user experience.
Online verification measures have become a central part of our digital interactions, serving both to protect users and to safeguard companies from potential threats. As we take a closer look at the message that instructs users to press and hold a button until it turns green, we see that this procedure is more than a simple test—it is a critical checkpoint to ensure that human users, and not automated bots, are in control of digital interactions.
The Genesis of Security Verification Protocols
Before the digital explosion, verifying the authenticity of an individual was a straightforward process involving physical presence or direct interaction with a human intermediary. However, as our reliance on web-based interactions increased, so did the need for automated systems that could effectively distinguish between human users and computer programs. The evolution of these systems has led us to today’s security verification processes—a series of steps that may include image-based puzzles, button presses, or even fingerprint scans. Each method is designed to weed out automated attacks and maintain the security integrity of online services.
The Role of Digital Identity in the Modern Legal Framework
Digital identity is no longer a vague concept, but a cornerstone of modern legal and administrative procedures. Verifying that an individual is indeed human is essential, not only for preventing fraud or cyber-attacks, but also for ensuring that legal procedures such as online contract negotiations or remote legal filings can be trusted. When a user is prompted with a message like “Please complete security verification,” this is not only a technical hurdle, but also a safeguard designed to protect the establishment of trust in virtual environments.
Legal experts point out that the verification process—often involving seemingly trivial instructions—carries a host of implications. For example, when users are asked to interact with a device (such as pressing and holding a button until it turns completely green), the simple act symbolizes a pledge of authenticity. Digital signatures and electronic proofs of identity have now become broadly recognized under e-signature laws, making these verification steps legally significant in a world where the line between physical and digital authorizations continues to blur.
Understanding and Interpreting the Security Prompt
The original message we are considering states: “Please complete security verification. This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you’re human. Please press and hold the button until it turns completely green.” On the surface, this message is straightforward. However, when we break it down and get into the subtle parts, each phrase is loaded with intention and meaning.
Breaking Down the Message: The Fine Points
- “Please complete security verification:” This opening line serves as an invitation to comply with a process designed with your safety in mind. The request is neutral yet direct, implying that a necessary checkpoint must be passed to proceed further.
- “This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you’re human:” Here we see an honest admission that the process might appear off-beat to the casual user. The phrase “confirm that you’re human” is especially important in today’s world, where automated hacks and malicious bot traffic are significant issues.
- “Press and hold the button until it turns completely green:” Although this is an instruction to follow a specific technical step, it is metaphorically significant. The transformation of the button’s state to green represents a visual affirmation of the human presence. It is a subtle yet effective method of providing assurance that the system’s checks have been met.
Each of these fragments contains its own set of tricky parts that may cause a moment of hesitation, especially among users who are not technologically savvy. However, understanding these little details helps to demystify the verification process, transforming what might seem overwhelming into a straightforward, secure transaction.
Comparing Verification Methods: Human Touch vs. Automation
The evolution from manual human checks to automated digital procedures encompasses both advancements in technology and changes in legal perspectives. The current trend toward automation is evident in every facet of online interactions, but it is important to note that there is still a need for human oversight. Automated systems are designed to make your way through standard verification processes quickly, yet they remain vulnerable to sophisticated attacks unless they are continuously updated with new security measures.
This balance between human oversight and automation is critical. On one hand, there is the necessity to protect sensitive information and prevent misappropriation of identity. On the other hand, overly complicated systems can frustrate users and potentially deter legitimate transactions. The legal community is on edge about this, as it is essential to strike the correct balance between protection and accessibility. How do we ensure that the steps required are super important for securing user data without unduly complicating the user experience?
Challenges and Legal Implications of Online Verification
Security verification measures, while undeniably useful, are not without their challenges. In an environment riddled with tension between access and privacy, the process of verifying every individual as human can become nerve-racking both for the user and the administrator of the system. The legal implications of these procedures are multifaceted, touching on issues ranging from data privacy to the enforceability of digital contracts.
Data Privacy: Ensuring Your Personal Information Stays Safe
One of the primary concerns with any digital verification process is data privacy. As users are asked to perform verification tasks, the system inevitably collects certain data points such as IP address information, as seen in the example “116.203.45.58 : a04b6365-84d1-4f9e-bf27-de26baa8.” Although seemingly innocuous, such data can be sensitive if mishandled.
Legal practitioners emphasize the need for stringent data privacy protocols. Here are some key considerations:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Consent | Ensuring users understand what data is being collected and how it will be used. |
| Data Storage | Implementing practices to securely store and manage data, reducing the risk of breaches. |
| Access Control | Defining strict protocols on who has access to this sensitive information. |
| Legal Compliance | Adhering to global data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA to protect users. |
The intricate balance of collecting enough information to maintain security without infringing on individual privacy rights is one of the more complicated pieces that administrators must get right. For those responsible for the legal oversight of digital platforms, these aspects are super important, ensuring that data is processed in a manner that is both secure and law-abiding.
Legal Accountability and User Trust
From a legal perspective, implementing security verification measures goes beyond mere technical necessity; it is about cultivating trust. The notion of accountability plays a significant role here. If an error occurs—if, for example, a user is mistakenly flagged as a bot or if the process hinders their access—the legal avenues for recourse may be limited or cumbersome.
Legal experts often stress that any system designed to protect users must also include a clear pathway for addressing disputes. The initial prompt often includes advice such as “If you believe this is an error, please contact our support team.” Although it appears as a minor footnote, it is a key component for maintaining a balance between required security protocols and user accessibility. In the absence of reliable dispute resolution mechanisms, users may find themselves trapped in a cycle of frustrating re-verification attempts, which can easily erode trust in the system.
Technical Aspects and the Human Factor
The core technical requirement of pressing and holding a button until it turns green is not arbitrary. Instead, it represents a blend of visual design and user interaction designed to leverage the physicality of a human response. By requiring an action that is difficult for a bot to simulate, the system effectively reduces the risk of automated abuse.
Decoding the Visual Cues and Their Legal Relevance
The instruction to “press and hold the button” might seem like a trivial task, yet its simplicity is its strength. The transformation of the button’s color to green serves as an instantaneous confirmation of user activity—an action that is difficult for automated systems to replicate. This type of verification process has evolved into a well-recognized symbol of digital authenticity that courts and regulatory bodies are increasingly likely to accept as evidence of a user’s endorsement.
Key reasons for this acceptance include:
- Traceability: The change in the button’s state is often logged, creating an audit trail that can be referred to in legal disputes.
- User Acknowledgment: The visible act of pressing the button assures both the system and the user of consent and intent.
- Technical Robustness: The method is straightforward yet effective in differentiating between human and machine, ensuring that the oversight mechanism is not easily bypassed.
For legal practitioners involved in cases regarding online consent and digital contracts, these technical details may seem like little distinctions, yet they carry significant weight in ensuring that digital systems are both secure and legally compliant.
Technical Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
No verification system is completely immune to errors or exploitation. While requiring users to press and hold a button until it turns green is a robust method for curbing most automated hacks, it is not entirely off the hook. Sophisticated bots might mimic such actions with increasing accuracy, therefore necessitating continuous improvements in the verification systems.
Some of the challenging bits in designing these systems include:
- Bot Evolution: As bots become more advanced, verification processes must also evolve to detect and prevent circumvention techniques.
- User Experience: Overly complex verification steps may deter legitimate users, thereby negatively impacting engagement on the platform.
- System Vulnerabilities: Any system collecting and processing user data must be carefully guarded against cyber-attacks that could exploit these very verification protocols.
Addressing these tangled issues requires a close collaboration between IT professionals, legal experts, and policymakers, ensuring that as the technology evolves, so too does the legal framework overseeing it. The result should be a system that efficiently confirms digital identity without compromising user rights or legal guarantees.
Balancing Accessibility and Security: A Legal Perspective
While automated security verification processes are undoubtedly essential, they also raise important issues about accessibility and fairness. There is a delicate balance that must be maintained between protecting the system from automated abuse and ensuring that human users can easily access the services they need. This balance becomes particularly significant when we factor in the legal implications of inadvertently restricting access to legitimate users.
User Accessibility in Security Protocols
Legal systems worldwide are increasingly recognizing that any security system should not only be secure but also user-friendly. For example, older users or those with disabilities might find it intimidating to complete a verification process that is overly complicated or unclear. In these cases, even the most secure system can end up being counterproductive if it alienates portions of the user community.
A few key points to consider when developing policy or systems involving security verifications include:
- User-Centered Design: Systems must be intuitive enough to allow users from all walks of life to complete the verification process.
- Accommodations for Differing Needs: Alternative verification methods may be needed for users with disabilities or those who may struggle with the standard procedure.
- Clear Communication: The language used in the verification prompt should be clear and free of technical jargon wherever possible, ensuring that the intent and instructions are unambiguous.
From a legal standpoint, ensuring that accessibility considerations are embedded in security verification systems is not just a best practice—it is becoming a regulatory requirement in many jurisdictions. This aligns with broader anti-discrimination and equal access mandates, which demand that digital services be inclusive for all users.
Legal Recourse and User Support
The original prompt includes a reference to contacting a support team if an error is believed to have occurred. This provision, while simple, is crucial from a legal perspective. It recognizes that even the best systems can fail, and it provides a clear, accessible pathway for users to seek redress. Without such measures, users might feel powerless in the face of technological errors, leading to broader issues of trust and accountability.
Key elements of an effective support and redress system include:
- Transparent Procedures: Users should be informed of the steps they can take if they experience difficulties during the verification process.
- Timely Responses: Legal and support teams must be prepared to act quickly when an error or dispute arises.
- Accountability Frameworks: There needs to be a clear protocol in place for documenting and addressing failures in the system, ensuring that any remedial measures are both prompt and effective.
The presence of such support measures not only improves user confidence but also bolsters the legal defensibility of the entire system. In cases where the security verification process is questioned in a legal dispute, a well-documented and accessible support framework can serve as evidence that all necessary steps were taken to ensure fairness and accountability.
The Future of Digital Verification in Legal Contexts
Looking ahead, the future of online verification and digital identity is likely to be shaped by rapid technological advancements, evolving legal standards, and growing public demand for secure, accessible digital interactions. Emerging technologies such as biometric verification, artificial intelligence, and blockchain-based identity solutions promise more seamless and secure methods of confirming human authenticity.
Embracing New Technologies for Verification
As technology continues to advance, legal frameworks will need to continually adapt to manage the emerging challenges and opportunities. The current system of pressing a button until it turns green may eventually be supplanted by more sophisticated methods. However, the underlying principle will remain the same: ensuring that the user is human, their identity verified, and their transaction secure.
Some projected advancements include:
- Biometric Identification: Fingerprint, facial recognition, and voice verification are already gaining traction. These methods promise higher accuracy and a lower risk of fraud.
- AI-Driven Security: Artificial intelligence can be used to analyze user behavior and detect subtle patterns that differentiate genuine users from automated scripts.
- Blockchain for Digital Identity: Blockchain technology may enable decentralized verification systems, offering transparency and security while removing the need for a single central authority.
Each of these advancements holds promise, yet they also come with their own set of complicated pieces and legal considerations. Ensuring that these new verification methods are developed responsibly and with adequate legal safeguards will be as critical as the technology itself.
Legal Legislations and Policy Adaptations
The intersection of rapid technological change and the legal domain has always been a hotbed for new policies and regulations. Governments around the world are increasingly focused on how to regulate digital identities, protect user data, and ensure that the rights of individuals are not compromised by automated systems. Drafting legislation that manages the fine points of digital security without stifling innovation is an ongoing challenge.
Some key policy areas include:
| Policy Area | Primary Focus |
|---|---|
| Digital Identity Verification | Establishing legal standards for technologies that verify human presence. |
| Data Protection | Ensuring that data collected during verification processes is stored securely and handled appropriately. |
| Accessibility Guidelines | Mandating that verification systems be inclusive and user-friendly for all demographics. |
| Consumer Redressal Mechanisms | Providing clear processes for users to report errors and seek resolution. |
A robust legal framework that addresses these areas is super important for ensuring that as technology evolves, users’ rights and security remain a top priority. Legislators and policy makers must continue to work closely with technologists and legal experts to craft policies that are fit for purpose in an increasingly digital society.
Conclusion: Reflecting on Security Verification as a Legal Safeguard
As we reflect on a simple message urging us to “complete security verification” by pressing and holding a button until it turns green, it becomes evident that such seemingly benign instructions encapsulate a wealth of legal, technical, and human considerations. What might be initially regarded as an overwhelming or nerve-racking requirement reveals a carefully designed process that seeks to protect users and maintain a trusted digital environment.
Understanding the subtle details behind each instruction—from ensuring data privacy to maintaining transparency in user support—allows us to appreciate the broader legal implications. The challenge lies in managing the tiny twists and turns of this process while accommodating the ever-growing demands of technological innovation and emerging legal standards.
Ultimately, whether you are a legal professional, a technology enthusiast, or a regular user navigating the online realm, it is crucial to recognize that security verification processes are not merely mechanical steps. They are a testament to our collective effort to forge a digital space where trust is built on clear, accountable, and human-centered practices. In embracing these practices, we can all contribute to enhancing the safety, fairness, and accessibility of our digital interactions.
The evolution of online verification is a journey filled with tricky parts and complicated pieces—the kind that demand a close, thoughtful look at every step. As we move forward, it will be essential to balance advanced technological solutions with the human factor, ensuring that every security check is implemented effectively while maintaining the user’s right to seamless access and robust legal protections.
In closing, the simple act of pressing a button until it turns green is more than just a user instruction; it is a symbol of our ongoing commitment to secure, inclusive, and legally sound digital environments. With continuous innovation and cooperation between legal and technological fields, we can look forward to a future where online verification processes are not only secure but also flexible enough to adapt to the evolving demands of society.
Originally Post From https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-04-medical-marijuana-cancer-patients-large.html
Read more about this topic at
OWASP DevSecOps Guideline – v-0.2
Interactive Authentication – Win32 apps